Neurobotics
Blended brain-machine control for human assistance using hybrid smart systems.

|
Funded by KU Leuven Internal Funds. |
Blended brain-machine control for human assistance using hybrid smart systems.

|
Funded by KU Leuven Internal Funds. |

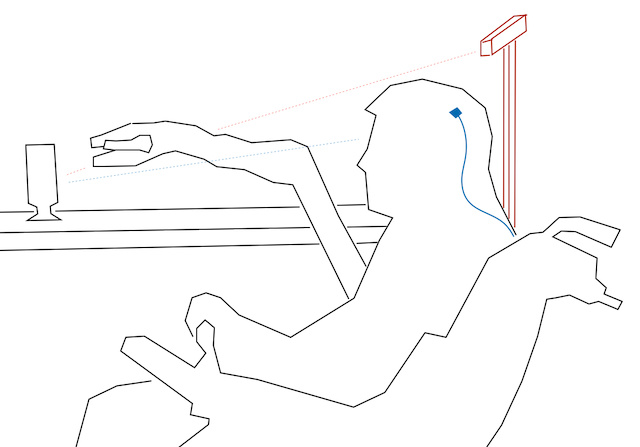
Project Purpose: We study the use of computer vision and machine learning to assist paralyzed patients who interact with the world with a robot arm that they command via neural implants. We develop means of predicting the intent of the patient, from the onset of a purely patient-controlled motion, and a visual understanding of the workspace and objects that the user could potentially wish to interact with.
Shared Robot Control
Our first publication (Song et al., 2024). addresses the problem of (a) predicting the trajectory of an arm reaching motion, based on a few seconds of the motion’s onset, and (b) leveraging this predictor to facilitate shared-control manipulation tasks, by reducing the operator’s cognitive load through assistance in their anticipated direction of motion. Our novel intent estimator, dubbed the Robot Trajectron (RT), produces a probabilistic representation of the robot’s anticipated trajectory based on its recent position, velocity and acceleration history. By taking arm dynamics into account, RT can capture the operator’s intent better than other SOTA models that only use the arm’s position, making it particularly well-suited to assist in tasks where the operator’s intent is susceptible to change. We derive a novel shared-control solution that combines RT’s predictive capacity to a representation of the locations of potential reaching targets. Our experiments demonstrate RT’s effectiveness in both intent estimation and shared-control tasks. We will make the code and data supporting our experiments publicly available on our GitLab server.
Scene Understanding
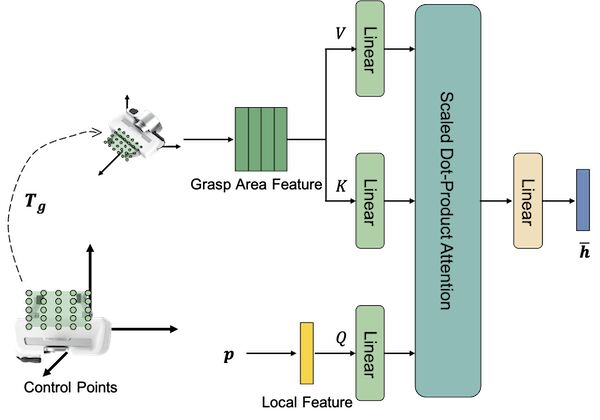
There are two dominant approaches in modern robot grasp planning: dense prediction and sampling-based methods. Dense prediction calculates viable grasps across the robot’s view but is limited to predicting one grasp per voxel. Sampling-based methods, on the other hand, encode multi-modal grasp distributions, allowing for different grasp approaches at a point. However, these methods rely on a global latent representation, which struggles to represent the entire field of view, resulting in coarse grasps. To address this, we introduce Implicit Grasp Diffusion (IGD) (Song et al., 2024), which combines the strengths of both methods by using implicit neural representations to extract detailed local features and sampling grasps from diffusion models conditioned on these features. Evaluations on clutter removal tasks in both simulated and real-world environments show that IGD delivers high accuracy, noise resilience, and multi-modal grasp pose capabilities. Our code is freely available.
 Bib
Bib PDF
PDF Video
Video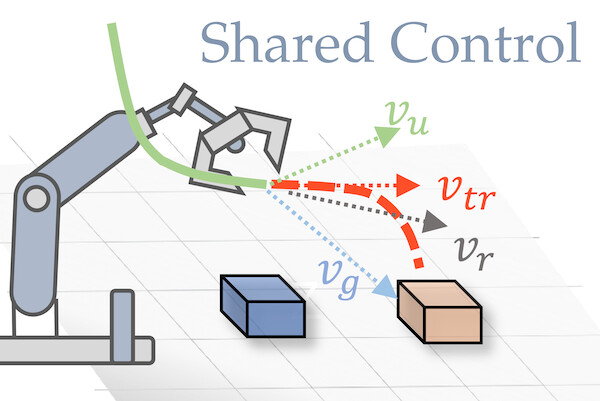
 DOI
DOI